In this article, you will discover the key to a strong immune system: the best vitamins. Learn about the vitamins that can help boost your body’s defense mechanisms and keep you healthy. Whether you’re looking for natural remedies or want to ensure you’re getting all the essential nutrients, this article will guide you through the top vitamins that can support your immune system. Say goodbye to frequent colds and sluggishness, and say hello to a healthier you. Let’s explore the world of immune-boosting vitamins together!

This image is property of Amazon.com.
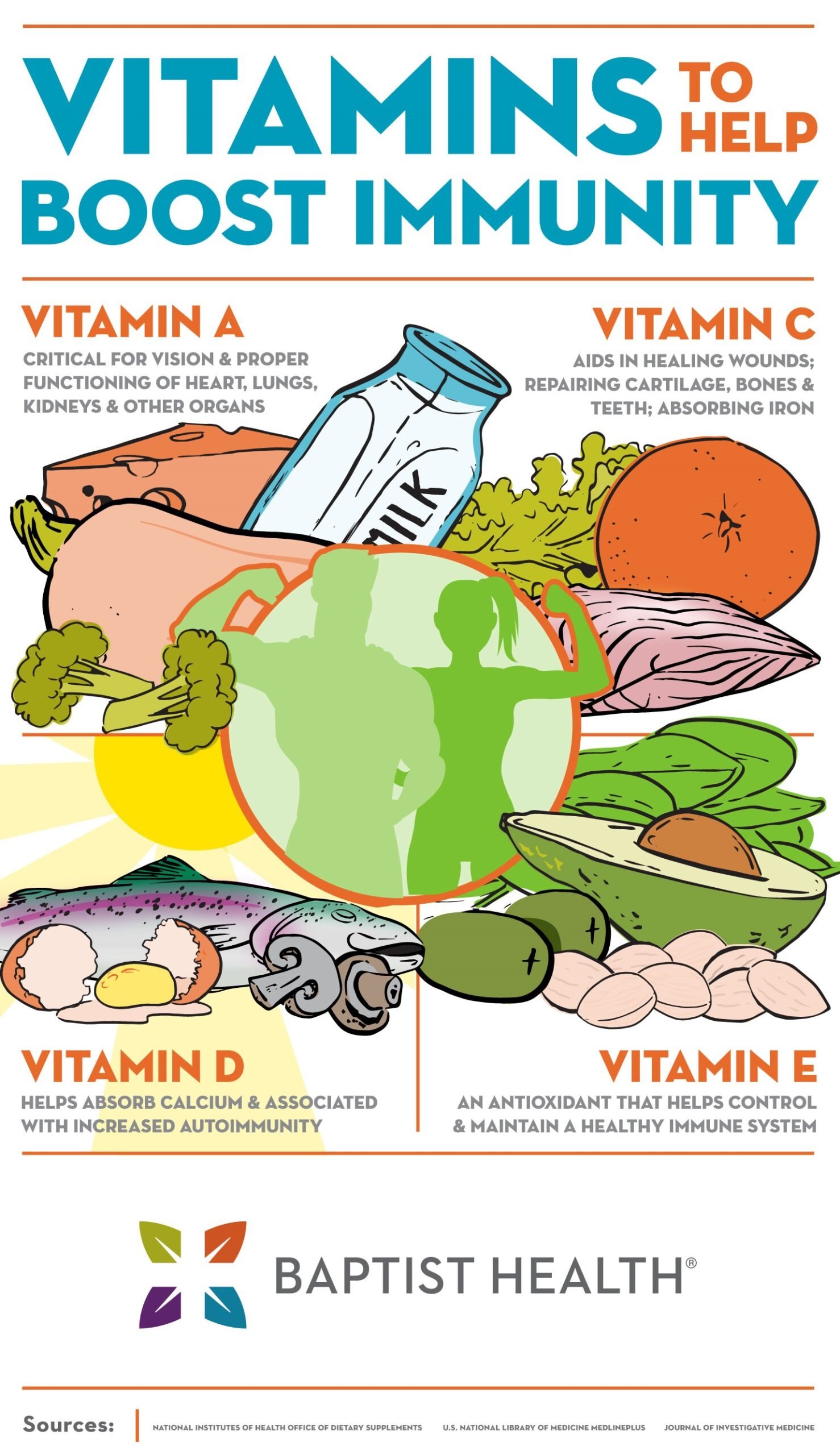
Vitamin C
Benefits of vitamin C for the immune system
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, plays a crucial role in supporting and strengthening the immune system. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by harmful free radicals. Vitamin C also plays a vital role in the production of collagen, a protein that aids in wound healing and the maintenance of healthy skin, which serves as a barrier against pathogens.
Additionally, vitamin C enhances the function of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which help defend the body against infections. It stimulates the production and activity of these immune cells, thereby improving the body’s ability to fight off harmful bacteria and viruses.
Food sources of vitamin C
To ensure an adequate intake of vitamin C, it is important to incorporate a variety of foods rich in this vitamin into your diet. Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, are well-known sources of vitamin C. Other fruits like strawberries, kiwi, and papaya also provide significant amounts of this essential vitamin. Vegetables like red and green bell peppers, broccoli, and spinach are excellent sources as well.
Recommended daily intake of vitamin C
The recommended daily intake of vitamin C varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 75-90 milligrams. However, in times of illness or stress, the daily intake may need to be increased to support immune function. It is important to note that excess amounts of vitamin C are usually excreted by the body, so it is generally safe to consume higher doses through diet or supplements.
Potential side effects
While vitamin C is generally considered safe, consuming excessive amounts may lead to gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps. These side effects are typically mild and can be avoided by sticking to the recommended daily intake. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Vitamin D
Role of vitamin D in immune health
Vitamin D is a unique nutrient that functions both as a vitamin and a hormone. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of the immune system, as it helps regulate the activity and function of immune cells. Vitamin D enhances the production of antimicrobial peptides, which are substances that help fight off harmful bacteria and viruses.
Furthermore, vitamin D supports the development and function of immune cells, such as T-cells and B-cells, which are essential for recognizing and eliminating pathogens. It also assists in reducing inflammation, which is an important aspect of immune response.
Sources of vitamin D
The primary source of vitamin D is sunlight. When exposed to sunlight, the skin produces vitamin D. However, obtaining sufficient vitamin D solely through sunlight can be challenging, especially in regions with limited sun exposure or during winter months. Therefore, it is important to incorporate dietary sources of vitamin D into your daily routine.
Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, are excellent sources of vitamin D. Additionally, fortified products like milk, orange juice, and cereals are commonly enriched with vitamin D. Some mushrooms also naturally contain vitamin D.
Recommended daily intake of vitamin D
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on age, gender, and individual circumstances. Generally, for adults, the recommended daily intake is around 600-800 International Units (IU). However, higher doses may be necessary for individuals with limited sun exposure or those at higher risk of deficiency. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Potential risks and side effects
Excessive intake of vitamin D through supplements can lead to toxicity, known as hypervitaminosis D. This can cause various symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and kidney problems. It is important to follow the recommended daily intake and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new vitamin D supplementation regimen.
This image is property of www.baptisthealth.com.
Vitamin E
Importance of vitamin E for immune function
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system by protecting its cells from oxidative stress. It neutralizes free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and impair the function of the immune system. By reducing oxidative stress, vitamin E helps promote the overall health and efficiency of the immune system.
Food sources rich in vitamin E
To ensure an adequate intake of vitamin E, it is important to include foods that are rich in this vitamin in your diet. Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, sunflower seeds, and peanuts, are excellent sources of vitamin E. Vegetable oils, including sunflower, wheat germ, and safflower oil, are also rich in this essential nutrient. Additionally, green leafy vegetables, like spinach and kale, are good sources of vitamin E.
Recommended daily intake of vitamin E
The recommended daily intake of vitamin E varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 15 milligrams. It is important to note that excessive intake of vitamin E through supplements may increase the risk of bleeding, so it is advisable to stick to the recommended daily intake.
Possible adverse effects
Consuming excessive amounts of vitamin E through supplements can lead to potential adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances, fatigue, and muscle weakness. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen and to obtain vitamin E through a balanced diet whenever possible.
Vitamin A
Role of vitamin A in supporting the immune system
Vitamin A plays a vital role in supporting the immune system by promoting the maintenance and function of various immune cells. It helps regulate the production and activity of immune cells, such as lymphocytes and neutrophils, which play a crucial role in defending the body against infections. Vitamin A also aids in the production of antibodies, which are proteins that help identify and neutralize harmful pathogens.
Food sources of vitamin A
To obtain an adequate amount of vitamin A, it is important to include a variety of foods rich in this vitamin in your diet. Animal sources, such as liver, fish, and dairy products, are excellent sources of vitamin A. Plant sources like sweet potatoes, carrots, and spinach also provide significant amounts of this essential nutrient.
Recommended dietary allowance for vitamin A
The recommended dietary allowance for vitamin A varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 700-900 micrograms of retinol activity equivalents (RAE). It is important to note that excessive intake of vitamin A through supplements, especially from animal-based sources, can be harmful. Therefore, it is recommended to obtain vitamin A through a balanced diet whenever possible.
Potential risks of excessive vitamin A intake
Consuming excessive amounts of vitamin A, especially in the form of supplements, can lead to vitamin A toxicity. This can cause symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, blurred vision, and even liver damage. Pregnant women should take extra caution, as high levels of vitamin A can harm the developing fetus. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new vitamin A supplementation regimen.

This image is property of pickyeaterblog.com.
Vitamin B6
Benefits of vitamin B6 for immunity
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system. It is involved in the production and activation of immune cells, such as lymphocytes and antibodies, which help defend the body against infections. Additionally, vitamin B6 assists in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to immune cells throughout the body.
Sources of vitamin B6
There are several food sources that are rich in vitamin B6. Poultry, such as chicken and turkey, is a good source of this essential vitamin. Fish, such as salmon and tuna, as well as meat products like pork and beef, also provide significant amounts of vitamin B6. Additionally, plant-based sources like bananas, chickpeas, and sunflower seeds contain vitamin B6.
Daily recommended intake of vitamin B6
The daily recommended intake of vitamin B6 varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 1.3-1.7 milligrams. It is important to note that excessive intake of vitamin B6 through supplements can lead to nerve damage, so it is advisable to stick to the recommended daily intake.
Possible side effects or interactions
Taking high doses of vitamin B6 supplements for an extended period of time may lead to nerve toxicity, causing symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and difficulty walking. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Vitamin B12
Importance of vitamin B12 for immune function
Vitamin B12 is essential for the normal functioning of the immune system. It plays a crucial role in the production and maturation of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which are responsible for defending the body against infections. Vitamin B12 also aids in the production of DNA, which is vital for the proper development and activity of immune cells.
Food sources rich in vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods. Meat, such as beef, chicken, and fish, is an excellent source of this essential nutrient. Shellfish, such as clams and mussels, also provide significant amounts of vitamin B12. Additionally, dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt contain vitamin B12. For those following a plant-based diet, fortified plant-based milk and cereals can be good sources of vitamin B12.
Recommended daily intake of vitamin B12
The recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 varies depending on age and individual circumstances. For most adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 2.4 micrograms. However, individuals with certain medical conditions or following specific dietary patterns may require higher doses. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Potential risks of vitamin B12 deficiency
Deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to various health issues, including a weakened immune system. Common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Long-term deficiency can cause serious neurological problems. Therefore, it is important to ensure an adequate intake of vitamin B12 through diet or supplementation, especially for individuals following a plant-based diet or those with certain medical conditions.
This image is property of www.byrdie.com.
Folate
Role of folate in immune system support
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 or folic acid, is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. It plays a crucial role in the production and maturation of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting off infections. Folate also assists in DNA synthesis and repair, which is important for the proper development and activity of immune cells.
Sources of folate
There are several food sources that are rich in folate. Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are excellent sources of this essential nutrient. Beans and legumes, like lentils and chickpeas, also provide significant amounts of folate. Furthermore, citrus fruits, avocados, and fortified grains are good sources of folate as well.
Recommended dietary allowance for folate
The recommended dietary allowance for folate varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 400-600 micrograms of dietary folate equivalents (DFE). However, pregnant women have higher folate requirements to support proper fetal development, typically around 600-800 micrograms of DFE. It is important to obtain folate through a balanced diet and, if necessary, consult with a healthcare professional regarding supplementation.
Potential risks of folate deficiency
Deficiency of folate can lead to various health complications, including a weakened immune system. Common symptoms of folate deficiency include fatigue, weakness, and poor immune response. Folate deficiency is also associated with an increased risk of certain birth defects in pregnant women. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of folate through a balanced diet or supplementation, especially for individuals at higher risk of deficiency.
Iron
Connection between iron and immune health
Iron is an important mineral that plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of the immune system. It is involved in the production and activity of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which help defend the body against infections. Iron also aids in the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to immune cells throughout the body.
Food sources of iron
There are two forms of dietary iron: heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron, found in animal-based sources, is more easily absorbed by the body. Good sources of heme iron include red meat, poultry, and seafood. Non-heme iron, found in plant-based sources, is less easily absorbed. Plant-based sources of iron include legumes, dark leafy greens, tofu, and fortified cereals.
Recommended daily intake of iron
The recommended daily intake of iron varies depending on age, gender, and individual circumstances. For most adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 8-18 milligrams. However, women of childbearing age and individuals with certain medical conditions may require higher doses. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Possible risks and side effects
Consuming excessive amounts of iron through supplements can lead to iron toxicity, known as hemochromatosis. Symptoms of iron toxicity include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It is important to stick to the recommended daily intake and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new iron supplementation regimen.

This image is property of www.baptisthealth.com.
Zinc
Importance of zinc for a strong immune system
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in supporting a strong immune system. It is involved in the development and function of immune cells, such as white blood cells and natural killer cells, which help protect the body against infections. Zinc also plays a crucial role in the production and maturation of antibodies, which are proteins that target and neutralize harmful pathogens.
Sources of zinc
There are several food sources that are rich in zinc. Animal-based sources, such as oysters, beef, and poultry, are excellent sources of this essential mineral. Other sources include seafood, dairy products, and fortified cereals. Additionally, plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds also provide significant amounts of zinc.
Recommended daily intake of zinc
The recommended daily intake of zinc varies depending on age and gender. For most adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 8-11 milligrams for males and around 8 milligrams for females. However, pregnant or lactating women may require higher doses. It is important to obtain zinc through a balanced diet or consult with a healthcare professional regarding supplementation.
Possible adverse effects of zinc deficiency
Zinc deficiency can impair immune function and increase susceptibility to infections. Common symptoms of zinc deficiency include frequent infections, delayed wound healing, and impaired growth in children. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of zinc through a balanced diet or supplementation, especially for individuals at higher risk of deficiency.
Selenium
Role of selenium in supporting immune function
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that plays a crucial role in supporting immune function. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by harmful free radicals. Selenium also enhances the production and activity of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which help defend the body against infections.
Food sources rich in selenium
There are several food sources that are rich in selenium. Brazil nuts are the highest dietary source of selenium. Other sources include seafood, such as oysters and tuna, as well as meat products like chicken and beef. Whole grains, like wheat and rice, and plant-based sources like beans and legumes also provide selenium.
Daily recommended intake of selenium
The daily recommended intake of selenium varies depending on age and gender. For most adults, the recommended daily intake is typically around 55-70 micrograms. It is important to note that excessive intake of selenium can be harmful, so it is advisable to obtain selenium through a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen.
Potential risks of excessive selenium consumption
Consuming excessive amounts of selenium through supplements can lead to selenium toxicity, known as selenosis. This can cause symptoms such as gastrointestinal disturbances, hair loss, and even neurological issues. It is important to follow the recommended daily intake and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new selenium supplementation regimen.
In conclusion, a balanced and nutritious diet, rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals, is essential for maintaining a strong and healthy immune system. Vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin A, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, folate, iron, zinc, and selenium all play essential roles in supporting immune function. Incorporating a wide range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products, into your diet is the best way to ensure an adequate intake of these vital nutrients. However, if you have specific concerns about your nutrient intake, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized recommendations to support your immune health.
