Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. From maintaining strong bones and muscles to supporting a healthy heart and regulating blood sugar levels, the benefits of magnesium supplements are nothing short of amazing. Not only can they help alleviate migraines and reduce stress, but they also contribute to better sleep and improved mood. So, if you’re looking to boost your health and enhance your daily life, it’s worth considering incorporating magnesium supplements into your routine. Discover how this mineral powerhouse can make a significant difference in your overall wellness.

This image is property of www.health.com.
Magnesium and its Importance
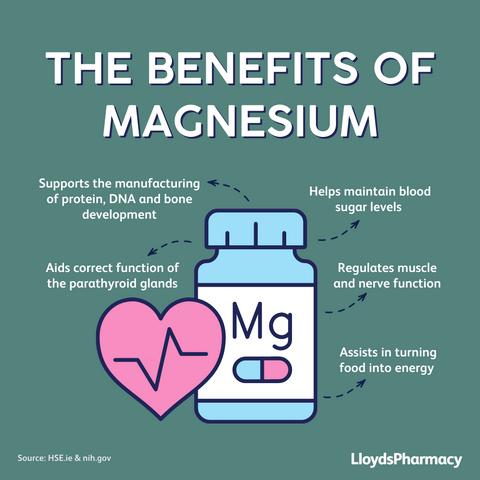
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body, making it necessary for various bodily functions. From supporting heart health to promoting digestive functions, magnesium truly lives up to its reputation as a powerhouse nutrient.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a mineral that is found abundantly in the human body, particularly in the bones, muscles, and soft tissues. It is involved in various physiological processes, including energy production, protein synthesis, and DNA synthesis. Magnesium is also vital for the proper functioning of enzymes and the transportation of ions across cell membranes.
Importance of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is involved in numerous bodily functions, making it crucial for overall health and well-being. Some of the key roles of magnesium in the body include:
- Regulating blood pressure: Magnesium helps relax and dilate blood vessels, thereby helping to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
- Supporting heart health: Magnesium contributes to the proper functioning of the heart muscles and helps prevent heart disease.
- Enhancing bone strength: Magnesium aids in bone formation and mineralization, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Relieving muscle cramps: Magnesium plays a role in muscle contraction and relaxation, which can help reduce the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps.
- Supporting mental health: Magnesium has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, alleviate anxiety and stress, and improve sleep quality.
- Promoting digestive health: Magnesium helps relieve constipation, improve gut motility, and even treat gastrointestinal disorders.
- Managing diabetes: Magnesium plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels, increasing insulin sensitivity, and preventing diabetic complications.
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, can have a wide range of symptoms and can significantly impact overall health. It is important to be aware of the common signs of magnesium deficiency and understand the health conditions that can be linked to inadequate magnesium levels.
Common Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
Some of the common signs and symptoms of magnesium deficiency include:
- Fatigue and weakness: Magnesium is involved in energy production, so low levels can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
- Muscle cramps and spasms: Inadequate magnesium levels can result in muscle cramps, spasms, and even restless leg syndrome.
- Irregular heartbeat: Magnesium helps regulate heart rhythm, so a deficiency can cause palpitations and irregular heartbeat.
- High blood pressure: Magnesium plays a role in relaxing blood vessels, so low levels can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
- Mood changes: Magnesium deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and irritability.
- Poor digestion: Insufficient magnesium levels can lead to digestive issues such as constipation, nausea, and poor appetite.
Health Conditions Linked to Magnesium Deficiency
In addition to the common signs mentioned above, magnesium deficiency has also been linked to various health conditions, including:
- Osteoporosis: Magnesium is essential for calcium absorption and bone mineralization, so inadequate levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Asthma: Low magnesium levels have been associated with an increased risk of developing asthma and worsening symptoms in individuals with existing asthma.
- Type 2 diabetes: Magnesium plays a role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, so deficiency can contribute to the development and progression of type 2 diabetes.
- Migraines: Research suggests that low magnesium levels may be associated with an increased frequency and severity of migraines.
- Fibromyalgia: Magnesium deficiency has been observed in individuals with fibromyalgia, a chronic pain disorder.
- Preeclampsia: Pregnant women with low magnesium levels may have an increased risk of developing preeclampsia, a serious complication characterized by high blood pressure.
How to Determine Magnesium Levels in the Body
If you suspect you may have a magnesium deficiency, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can accurately assess your magnesium levels. Diagnostic tests such as a blood test or urine test can be used to determine magnesium status. However, it is important to note that these tests may not always provide a complete picture of magnesium levels, as the majority of magnesium is stored in the bones and cells.
This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Magnesium Supplements as a Solution
In cases where magnesium deficiency is confirmed, magnesium supplements can be a convenient and effective solution to replenish magnesium stores in the body. There are different forms of magnesium supplements available, and understanding the recommended dosage and safety precautions is crucial for optimal supplementation.
Different Forms of Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics and benefits. Some common forms include:
- Magnesium citrate: This form of magnesium is highly absorbable and is often utilized to support digestive health and relieve constipation.
- Magnesium glycinate: Magnesium glycinate is well-tolerated and highly absorbable, making it a popular choice for improving sleep quality and managing stress.
- Magnesium oxide: Although it has a lower absorption rate, magnesium oxide is often used to relieve heartburn and indigestion.
- Magnesium chloride: This form of magnesium is commonly used in topical applications such as magnesium oil for muscle relaxation and pain relief.
- Magnesium sulfate: Known as Epsom salt, magnesium sulfate is often used in baths to soothe sore muscles and promote relaxation.
Recommended Daily Dosage of Magnesium
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides the following guidelines for magnesium intake:
- Adult males (19+ years): 400-420 mg
- Adult females (19+ years): 310-320 mg
- Pregnant females (19-50 years): 350-360 mg
- Breastfeeding females (19-50 years): 310-320 mg
It is important to note that individual magnesium needs can vary based on factors such as physical activity, medical conditions, and medications. Consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Safety Precautions for Magnesium Supplement Use
While magnesium supplements are generally safe for most individuals when used as directed, there are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Speak to your healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medications.
- Follow the recommended dosage guidelines provided on the supplement packaging or as advised by a healthcare professional.
- Be aware of potential drug interactions. Magnesium supplements may interact with certain medications, such as antibiotics, diuretics, and osteoporosis medications. Consult with your healthcare professional if you are taking any medications to ensure there are no contraindications.
- Avoid excessive intake of magnesium supplements, as extremely high levels can lead to magnesium toxicity.
- If you experience any adverse effects or unusual symptoms after starting magnesium supplementation, discontinue use and consult with a healthcare professional.
Improving Heart Health
Heart health is of utmost importance, and magnesium plays a significant role in supporting the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. From regulating blood pressure to preventing heart disease, adequate magnesium levels are crucial for maintaining a healthy heart.
Regulating Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure by promoting the relaxation of blood vessels, reducing resistance, and improving blood flow. Several studies have found a positive correlation between magnesium intake and lower blood pressure levels. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods or supplements into your daily routine may contribute to better blood pressure management.
Preventing Heart Disease
Magnesium is involved in numerous processes that impact heart health and may help prevent heart disease. Certain studies have shown a link between low magnesium levels and an increased risk of coronary heart disease, arrhythmias, and other cardiovascular conditions. By maintaining optimal magnesium levels, you can potentially reduce the risk of heart disease and promote a healthy heart.
Managing Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining the electrical stability of the heart, which is essential for proper heart function. In cases where arrhythmias are related to magnesium deficiency, magnesium supplements may be recommended to restore adequate levels and promote a more regular heart rhythm.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Enhancing Bone Strength
Maintaining strong and healthy bones is essential for overall mobility and quality of life. Magnesium plays a pivotal role in bone health by promoting calcium absorption, regulating bone formation and mineralization, and reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Preventing Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by the loss of bone density and increased susceptibility to fractures. Magnesium assists in the conversion of vitamin D into its active form, which is necessary for calcium absorption. Adequate magnesium levels are crucial for maximizing calcium utilization and promoting optimal bone density. By ensuring sufficient magnesium intake, you can help prevent the development of osteoporosis and maintain strong bones.
Reducing the Risk of Fractures
Fractures, especially among older adults, can significantly impact quality of life and independence. Studies have shown a positive association between magnesium intake and bone mineral density, suggesting that adequate magnesium levels may help reduce the risk of fractures. Magnesium works synergistically with other nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, to support bone health and maintain bone strength.
Improving Bone Density
Maintaining proper bone density is important for overall bone health and fracture prevention. In addition to calcium and vitamin D, magnesium is a key nutrient involved in bone mineralization. Magnesium stimulates specific cells called osteoblasts, which are responsible for creating new bone tissue. By promoting healthy bone remodeling and mineralization, magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal bone density.
Relieving Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps can range from minor discomfort to excruciating pain, and they often occur due to factors such as dehydration, muscle fatigue, or nutrient deficiencies. Adequate magnesium levels are essential for proper muscle function, and magnesium supplementation may help reduce the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps.
Causes of Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps can be caused by various factors, including:
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to electrolyte imbalances, including magnesium deficiency, which may trigger muscle cramps.
- Overexertion: Engaging in intense physical activity without proper warm-up, stretching, or conditioning can increase the risk of muscle cramps.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Magnesium, along with other minerals such as potassium and calcium, is crucial for muscle contraction and relaxation. Inadequate levels of these minerals can contribute to muscle cramps.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics and certain blood pressure medications, may increase the risk of muscle cramps.
Magnesium’s Role in Muscle Contraction and Relaxation
Magnesium is a key player in muscle contraction and relaxation processes. It helps regulate calcium levels in muscle cells, which is essential for proper muscle function. Adequate magnesium levels can promote the optimal balance between calcium and magnesium, preventing muscle spasms and cramps. By ensuring sufficient magnesium intake, you can help support healthy muscle function and reduce the occurrence of muscle cramps.
Reducing the Frequency and Intensity of Muscle Cramps
If you experience frequent muscle cramps, particularly during physical activity or at night, magnesium supplementation may be beneficial. By replenishing magnesium stores in the body, you can help reduce the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps. Additionally, incorporating magnesium-rich foods such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds into your diet can help maintain optimal magnesium levels and support overall muscle health.

This image is property of www.swansonvitamins.com.
Supporting Mental Health
Maintaining good mental health is crucial for overall well-being and quality of life. Research suggests that magnesium supplementation may offer benefits in reducing symptoms of depression, alleviating anxiety and stress, and improving sleep quality.
Reducing Symptoms of Depression
Depression is a common mental health condition that can have a significant impact on daily life. Studies have demonstrated a link between magnesium deficiency and an increased risk of depression. Magnesium plays a role in neurotransmitter function and regulation, including the production and release of serotonin, a hormone that contributes to mood regulation. By ensuring adequate magnesium intake, you may help reduce the risk of depression and alleviate its symptoms.
Alleviating Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are common experiences in today’s fast-paced and demanding world. Magnesium can help modulate the release of stress hormones and regulate the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is responsible for the body’s stress response. By supporting the body’s stress response system, magnesium supplementation may help alleviate anxiety and promote a calmer state of mind.
Improving Sleep Quality
Quality sleep is vital for overall health and well-being. Magnesium has been shown to play a role in sleep regulation and the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Adequate magnesium levels can help improve sleep quality, reduce sleep disturbances, and promote a more restful night’s sleep. If you struggle with sleep-related issues, magnesium supplementation may be beneficial in optimizing your sleep patterns.
Promoting Digestive Health
A healthy digestive system is crucial for the absorption of nutrients and overall well-being. Magnesium plays a role in various digestive processes and can help relieve constipation, improve gut motility, and even treat certain gastrointestinal disorders.
Relieving Constipation
Constipation is a common digestive issue characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficult passage of stools. Adequate magnesium levels are essential for maintaining proper bowel function and promoting regularity. Magnesium helps draw water into the intestines, softening the stools and facilitating smoother bowel movements. However, it is important to note that excessive magnesium supplementation can have a laxative effect, so it is crucial to follow dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent constipation.
Improving Gut Motility
Gut motility refers to the movement of food through the digestive tract. Adequate magnesium levels contribute to proper gut motility, preventing issues such as slowed digestion or gastrointestinal stasis. Magnesium supports the proper functioning of the muscles in the digestive tract, promoting efficient movement of food and waste products. By ensuring sufficient magnesium intake, you can help support healthy gut motility and optimize digestive function.
Treating Gastrointestinal Disorders
Magnesium has been utilized in the treatment of certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as acid reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Magnesium-based antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and provide relief from symptoms of acid reflux. Additionally, magnesium supplements may offer benefits in managing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) by promoting relaxation of the intestinal muscles and alleviating abdominal pain and discomfort.
This image is property of i.shgcdn.com.
Managing Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels and impaired insulin function. Magnesium plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and the prevention of diabetic complications.
Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
Magnesium is involved in carbohydrate metabolism and insulin action, making it essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Adequate magnesium intake has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By promoting proper glucose metabolism, magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels and contributes to overall diabetes management.
Increasing Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes and occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Magnesium is involved in insulin signaling and helps enhance insulin sensitivity. This means that sufficient magnesium levels can help improve the body’s utilization of insulin, resulting in better blood sugar control. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods or supplements into your diabetes management plan may provide additional support in maintaining optimal insulin sensitivity.
Preventing Diabetic Complications
Magnesium may help reduce the risk of diabetic complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can improve lipid profiles, reduce inflammation, and enhance endothelial function, all of which contribute to reducing the risk of diabetic complications. By maintaining adequate magnesium levels, you can potentially mitigate the long-term effects of diabetes and protect against associated health complications.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. From supporting heart health to promoting digestive functions, magnesium is involved in numerous physiological processes. Adequate magnesium levels are necessary for optimal bodily functions, and magnesium supplementation can be a convenient and effective solution for replenishing magnesium stores in the body. By prioritizing magnesium intake, you can support your heart, bones, muscles, mental health, digestive system, and even diabetes management. As with any dietary supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting magnesium supplementation to ensure it is appropriate for your specific needs.