As you age, maintaining proper nutrition becomes increasingly important for your overall health and well-being. With the right combination of foods, you can improve your energy levels, support your immune system, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. In this article, we will explore some valuable nutrition tips specifically tailored for seniors, helping you make informed choices about what to eat to support your senior health.
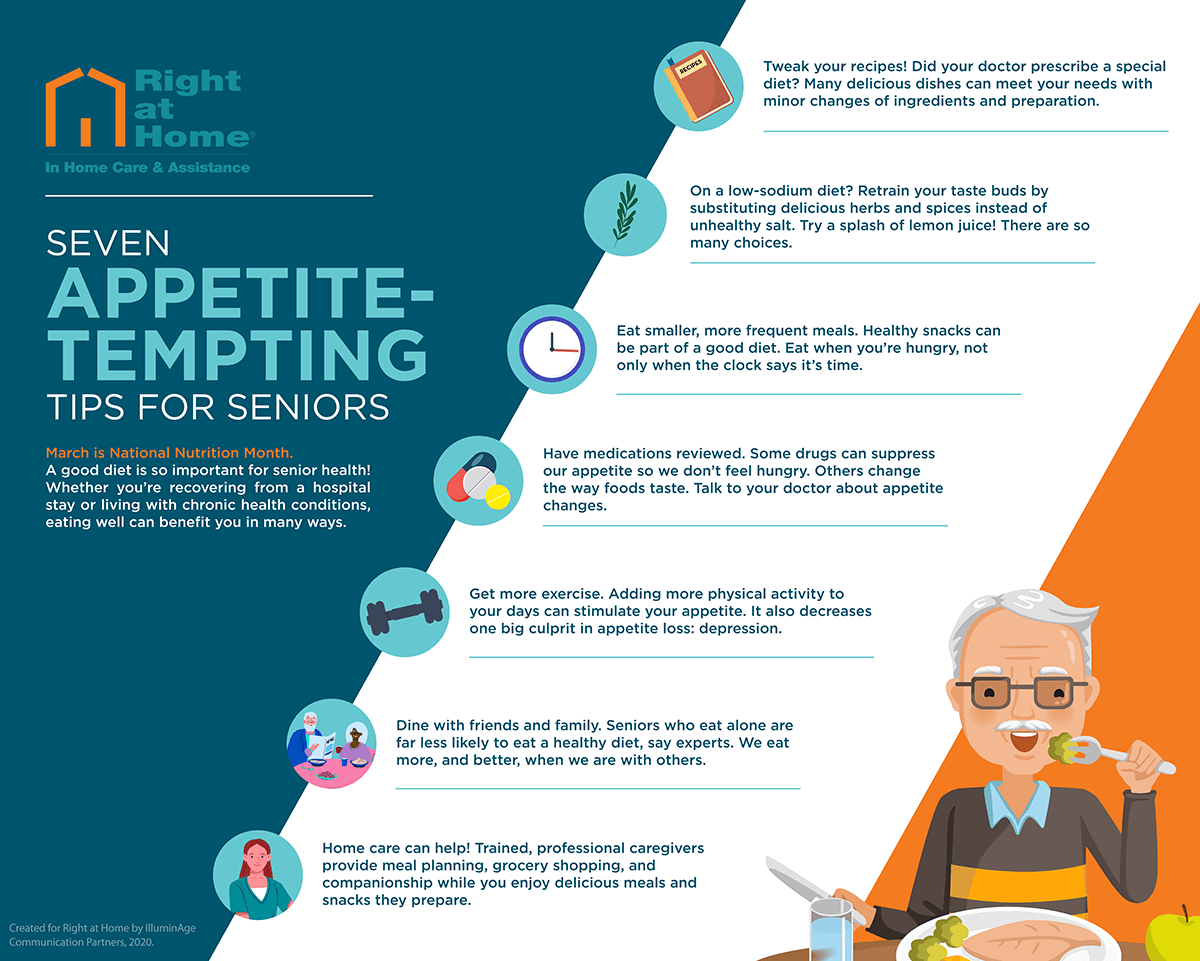
This image is property of www.rightathome.net.
Importance of Nutrition for Senior Health
As you age, it becomes increasingly important to pay attention to your nutrition and make sure you are getting the right nutrients for your body. Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in healthy aging, preventing chronic diseases, and maintaining a strong immune system. By following a balanced and nutrient-rich diet, you can support your overall health and well-being in your senior years.
Healthy Aging and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in healthy aging. As you get older, your body’s metabolism slows down, making it important to consume nutrient-dense foods that provide the necessary energy for proper bodily functions. A well-balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve cognitive function, and enhance your mood.
Preventing Chronic Diseases
A nutritious diet can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases commonly associated with aging, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet can provide a wide range of essential nutrients and antioxidants that help combat inflammation and oxidative stress, two factors implicated in the development of chronic diseases.
Maintaining a Strong Immune System
As you age, your immune system naturally weakens, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. However, a healthy diet can help boost your immune system and keep it functioning optimally. Consuming foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and zinc can enhance your immune response and help protect against infections. Additionally, maintaining a healthy gut by consuming fiber-rich foods can support the growth of beneficial bacteria and further strengthen your immune system.
Key Nutrients for Senior Health
Several key nutrients are particularly important for senior health. Including these nutrients in your diet can help support various bodily functions and promote overall well-being.
Fiber
Fiber is an essential nutrient for seniors as it aids in digestion, prevents constipation, and helps maintain a healthy weight. High-fiber foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily to optimize your digestive health.
Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium and vitamin D are crucial for maintaining healthy bones and preventing osteoporosis, a condition common in seniors. Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources of calcium, while sunlight exposure and fortified foods can provide vitamin D. Aim for a daily intake of 1200 milligrams of calcium and 800-1000 IU of vitamin D.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and supporting brain function. Cold-water fatty fish like salmon, trout, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s. If you don’t consume fish, consider adding flaxseeds, chia seeds, or walnuts to your diet.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining proper nerve function, producing red blood cells, and preventing anemia. As you age, your body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12 decreases, making supplementation or fortified foods necessary. Good sources of vitamin B12 include meat, fish, eggs, and fortified cereals.
Potassium
Potassium is a mineral that helps maintain healthy blood pressure, regulate fluid balance, and support proper muscle and nerve function. Including potassium-rich foods in your diet, such as bananas, oranges, avocados, and potatoes, can help maintain optimal potassium levels.
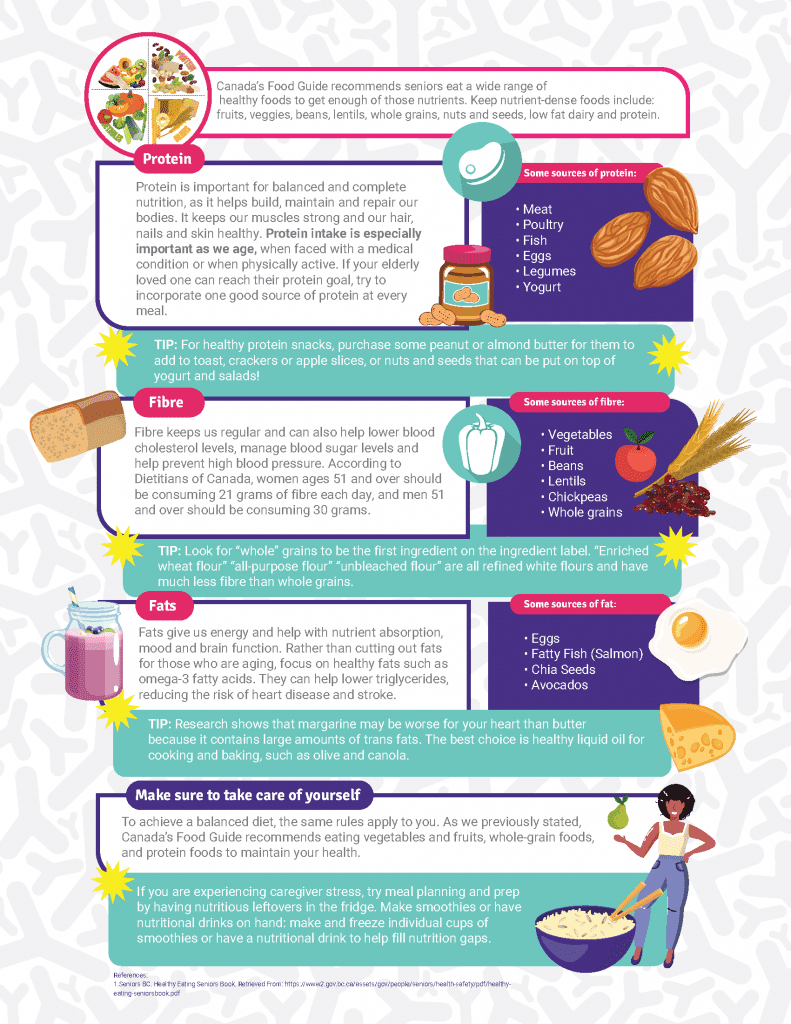
This image is property of cdhf.ca.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is critical for senior health and overall well-being. By making mindful choices and incorporating the following strategies into your eating habits, you can ensure you are providing your body with the nutrients it needs.
Choose Whole Foods
Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible. These foods are typically higher in nutrients and lower in additives, artificial ingredients, and added sugars. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins should be the foundation of your diet.
Focus on Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals, as different colors often signify different nutrients. Try to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables for maximum nutritional benefits.
Include Lean Protein Sources
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass, promoting wound healing, and supporting immune function. Choose lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, and low-fat dairy products. Aim for at least two servings of protein per day.
Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
Processed foods tend to be high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars. These can contribute to chronic diseases like heart disease, obesity, and diabetes. Limit your consumption of processed snacks, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is crucial for seniors, as the sensation of thirst can diminish with age. Aim to drink at least eight cups of water throughout the day. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, confusion, and other health complications, so make sure to drink water regularly.
Managing Portion Sizes
Proper portion control is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing overeating. The following strategies can help you manage portion sizes effectively.
Use a Smaller Plate
Using a smaller plate can trick your mind into thinking you are consuming a larger portion size. By reducing the size of your plate, you can naturally control the amount of food you eat. This simple trick can help prevent overeating and promote healthier serving sizes.
Listen to Your Hunger and Fullness Cues
Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness signals. Eat when you are hungry and stop when you are comfortably full. It can be helpful to eat slowly and savor each bite, allowing your brain to register when you’ve had enough food.
Be Mindful of Liquid Calories
Beverages like soda, juice, and sweetened coffee drinks can contribute a significant amount of unnecessary calories. Be mindful of liquid calories and opt for water, unsweetened tea, or other low-calorie beverages instead. These choices will help keep your calorie intake in check.
Take Your Time while Eating
Eating slowly and chewing your food thoroughly allows your body to digest food properly and helps control portion sizes. Taking your time while eating also gives your brain the chance to register feelings of fullness, preventing you from overeating.
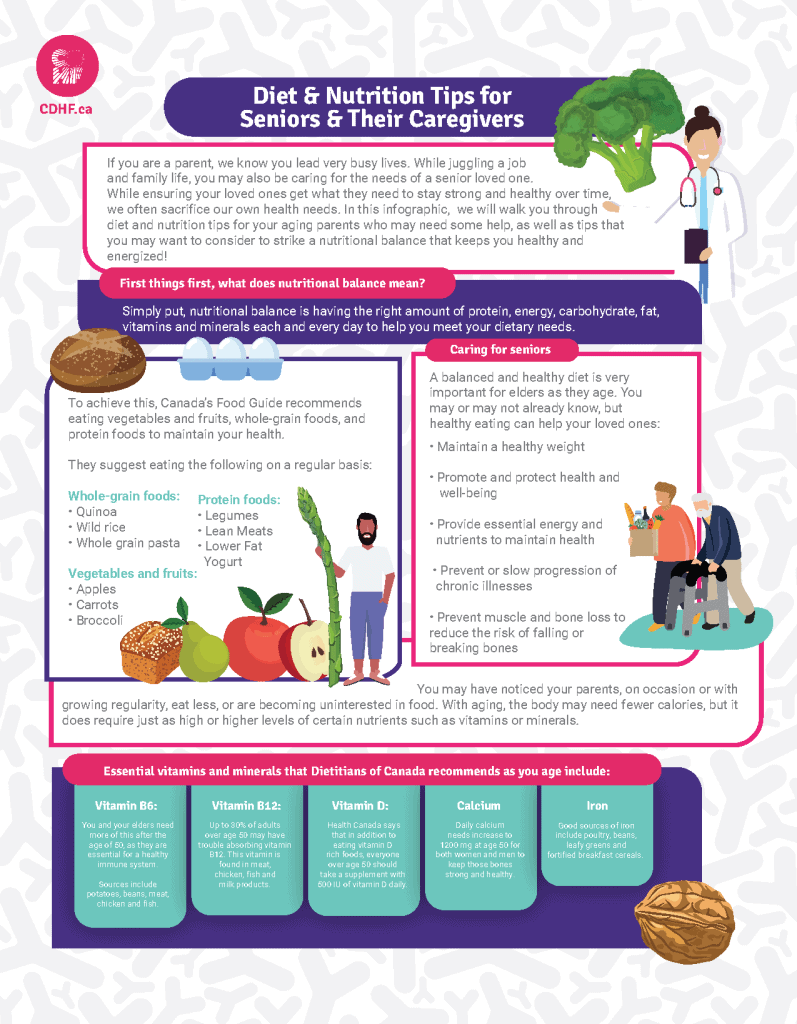
This image is property of cdhf.ca.
Strategies for Healthy Eating
Adopting healthy eating habits can be made easier with the following strategies in mind.
Plan and Prepare Meals in Advance
Planning and preparing meals in advance can help you make healthier choices and avoid reaching for unhealthy options when you’re hungry. Set aside time each week to plan your meals, create a grocery list, and prepare meals in advance. This way, you’ll always have nutritious options readily available.
Eat Regularly and Not Skip Meals
Maintain regular meal times and avoid skipping meals. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later in the day and may cause you to choose less healthy options. Aim for three balanced meals and incorporate healthy snacks as needed to keep your hunger satisfied throughout the day.
Control Sodium Intake
Excessive sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Limiting sodium intake is especially important for seniors. Avoid adding salt to your meals, choose low-sodium options, and season your food with herbs, spices, and lemon juice instead.
Eat a Variety of Foods
Eating a wide variety of foods ensures that you’re getting a range of nutrients in your diet. Try to include different colors, textures, and flavors in your meals to make them more enjoyable and nutritionally diverse.
Read Food Labels
Take the time to read food labels and understand what you’re consuming. Look out for hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive sodium content. Learning to decipher food labels can help you make informed choices and select healthier options.
Special Considerations for Seniors with Health Conditions
Seniors with specific health conditions should be mindful of certain dietary considerations to support their overall health and well-being.
Heart Disease and High Blood Pressure
For seniors with heart disease or high blood pressure, it is crucial to follow a low-sodium diet. In addition to controlling sodium intake, limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can help improve heart health. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can further support cardiovascular health.
Diabetes
Seniors with diabetes should focus on managing their blood sugar levels through portion control, carbohydrate monitoring, and regular blood sugar testing. Working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help create an individualized meal plan that best meets their needs.
Osteoporosis
Individuals with osteoporosis should prioritize calcium and vitamin D intake to support bone health. In addition to consuming calcium-rich foods, weight-bearing exercises and resistance training can help improve bone strength.
Foodborne Illnesses and Food Safety
Seniors are more susceptible to foodborne illnesses due to compromised immune systems. To reduce the risk, it is important to handle, store, and cook food properly. Avoid consuming undercooked meats, raw eggs, and unpasteurized dairy products. Washing hands frequently and cleaning surfaces are essential practices for food safety.
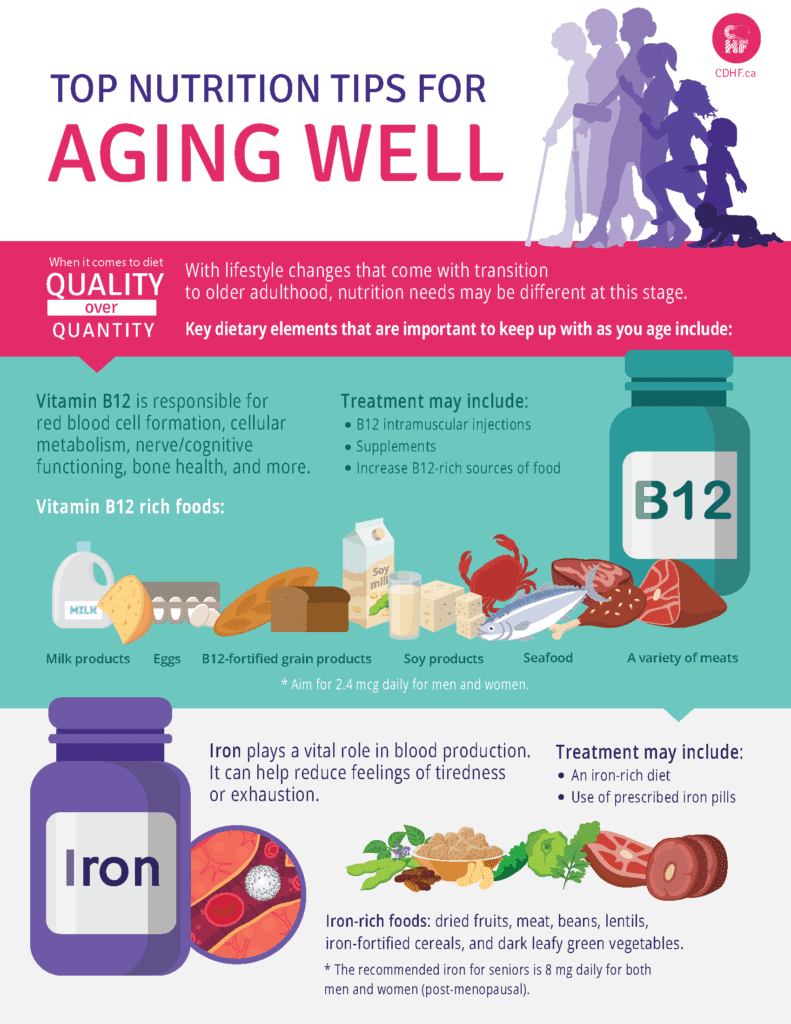
This image is property of cdhf.ca.
Promoting Digestive Health
Maintaining a healthy digestive system is crucial for seniors’ overall well-being. The following strategies can help promote digestive health.
Eat High-Fiber Foods
Aim to include high-fiber foods in your diet, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Fiber helps promote regular bowel movements, prevent constipation, and support a healthy gut microbiome.
Stay Active and Exercise
Regular physical activity can aid in digestion by stimulating intestinal contractions and preventing constipation. Engage in activities like walking, swimming, or yoga to support a healthy digestive system.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and incorporate hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables into your meals.
Managing Medications and Nutrient Interactions
Seniors often take multiple medications, and it is important to be aware of potential nutrient interactions. Consider implementing the following strategies to manage medication and nutrient interactions effectively.
Consult with a Healthcare Professional
Always consult with your healthcare professional or pharmacist regarding potential interactions between your medications and nutrients. They can provide guidance on any dietary modifications or supplements necessary to avoid adverse effects.
Consider Nutrient Supplements
In some cases, seniors may require nutrient supplements to meet their specific needs. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements to ensure they are necessary and safe for you.
Be Aware of Medication Side Effects
Certain medications can have side effects that affect appetite, taste perception, or nutrient absorption. Be mindful of any changes in your eating patterns or food preferences and discuss these changes with your healthcare professional.

This image is property of www.unlockfood.ca.
Eating for Mental and Emotional Well-being
Eating habits can also have a significant impact on your mental and emotional well-being. Consider the following strategies to support your overall mental health.
Include Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, dark chocolate, and green leafy vegetables, can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are linked to mental decline and mood disorders.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact cognitive function and mood. Limit your alcohol intake to moderate levels or seek guidance from a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Stay Socially Active
Maintaining social connections and engaging in social activities can have a positive impact on mental and emotional well-being. Enjoy meals with family and friends or consider joining community groups that share your interests.
Practice Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying full attention to your eating experience, savoring your food, and being aware of hunger and fullness cues. This practice can enhance enjoyment, reduce emotional eating, and improve your relationship with food.
Seek Professional Support if Needed
If you’re experiencing mental health concerns, such as depression or anxiety, it’s essential to seek professional support. Mental health professionals can provide valuable guidance and resources to help you navigate any challenges you may be facing.
Final Thoughts
As a senior, nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and well-being. By prioritizing a balanced diet, consuming key nutrients, managing portion sizes, following healthy eating strategies, and considering specific health conditions, you can support your overall health as you age. Remember to also prioritize your mental and emotional well-being through mindful eating, social connections, and seeking professional support when needed. By incorporating these practices and enjoying flexibility in your eating habits, you can ensure you’re eating for optimal senior health and continue to live an enjoyable and fulfilling life.
