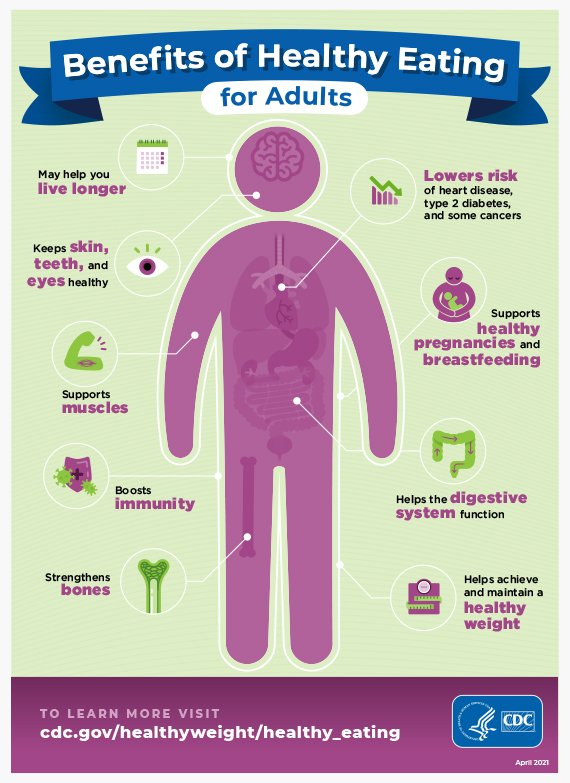
Maintaining a balanced diet is key in not only managing your weight effectively but also in ensuring overall health and well-being. As we all know, a balanced diet consists of consuming a variety of foods that provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support our body’s functions. By incorporating a well-rounded diet into your lifestyle, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, while also reducing the risk of chronic diseases and improving your energy levels. In this article, we will explore the importance of a balanced diet for weight management and why it should be a priority in your daily routine.
This image is property of static.sportzbusiness.com.
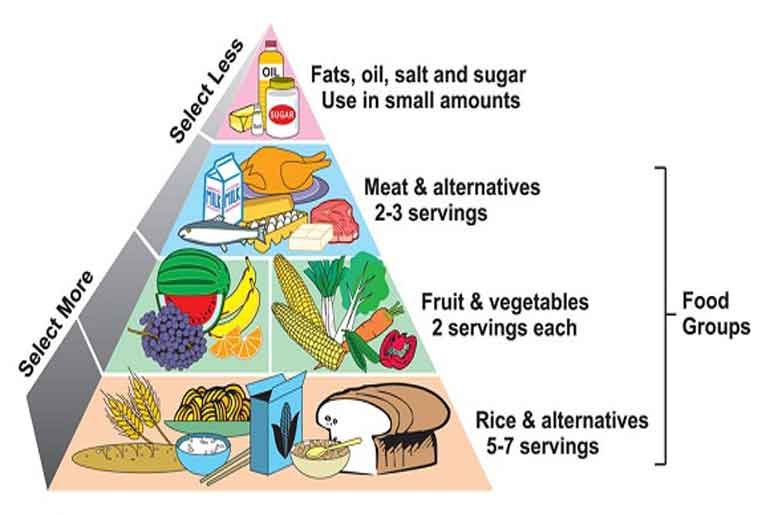
Definition of a Balanced Diet
The concept of a balanced diet
When we talk about a balanced diet, we refer to an eating plan that includes all the essential nutrients in the right proportions. It is a diet that provides the body with the necessary energy, vitamins, minerals, and other substances needed for optimal health and well-being. A balanced diet is key to maintaining a healthy weight and preventing chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Nutritional needs for weight management
Weight management involves achieving a healthy body weight through a combination of proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and a balanced lifestyle. The nutritional needs for weight management are different for each individual, as they depend on factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. However, there are some general guidelines that can help create a balanced diet for weight management.
Caloric Intake and Weight Management
Understanding caloric intake
Caloric intake refers to the number of calories consumed through food and drinks. The balance between the calories consumed and the calories burned determines whether an individual gains, maintains, or loses weight. Weight management revolves around finding the right balance to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Understanding caloric intake is crucial in this process.
The role of macronutrients in weight management
Macronutrients, namely carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are the main sources of calories in our diet. Each macronutrient plays a specific role in weight management. Carbohydrates provide energy, proteins build and repair tissues, and fats assist in various bodily functions. Balancing the intake of macronutrients is important to ensure an adequate supply of energy and nutrients while managing weight effectively.
This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
Importance of a Balanced Diet for Weight Loss
Creating a caloric deficit
Weight loss occurs when there is a caloric deficit, which means you consume fewer calories than you burn. However, it is essential to create this deficit in a healthy and sustainable way. A balanced diet allows you to reduce caloric intake while still meeting your nutritional needs. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods and controlling portion sizes, you can create a caloric deficit without depriving your body of essential nutrients.
Preventing nutrient deficiencies
Restrictive diets often lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can have negative effects on overall health and weight management. A balanced diet ensures you are getting all the necessary vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients, preventing deficiencies. Ensuring an adequate intake of nutrients is crucial for the body to function optimally and support weight loss efforts in a safe and healthy manner.
Regulating appetite and cravings
Maintaining a balanced diet can help regulate appetite and cravings, which are common challenges when trying to lose weight. By including foods that are rich in fiber, high-quality proteins, and healthy fats, you can increase satiety and reduce the desire for unhealthy snacks. A balanced diet keeps you feeling satisfied for longer periods and helps maintain control over your food choices.
Nutrients Essential for Weight Management
Proteins
Proteins are essential nutrients for weight management. They are the building blocks of cells and are involved in various functions in the body. Including sufficient protein in your diet can help maintain muscle mass, which is important for a healthy metabolism. Additionally, protein-rich foods can increase satiety and reduce cravings, contributing to weight loss efforts.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal, and choosing the right ones is crucial for weight management. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, provide essential nutrients and fiber, promoting satiety and regulating blood sugar levels. On the other hand, refined carbohydrates, like sugary foods and processed grains, should be limited as they can lead to weight gain.
Fats
Fats are often misunderstood and associated with weight gain, but they play a vital role in weight management. Including healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can promote satiety, enhance nutrient absorption, and support overall health. It is important to choose unsaturated fats while limiting saturated and trans fats, which are more likely to contribute to weight gain and health issues.
Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot fully digest. It adds bulk to the diet, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps control appetite. High-fiber foods are generally lower in calories and can make you feel fuller for longer, aiding in weight management. Including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your diet can significantly increase your fiber intake.
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential for various bodily functions and supporting weight management. Healthy and balanced eating ensures that you get an adequate supply of vitamins. Vitamin D, for example, plays a role in regulating body weight, while the B vitamins are involved in energy metabolism. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products in your diet can help meet your vitamin needs.
Minerals
Just like vitamins, minerals are essential for overall health and weight management. Minerals such as calcium, iron, and magnesium are involved in various metabolic processes, while others, like zinc and chromium, play a role in regulating appetite and blood sugar levels. A balanced diet that includes a wide range of nutrient-dense foods provides the necessary minerals for optimal weight management.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are substances that help protect the cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Including antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, in your diet is essential for weight management. Antioxidants may help reduce inflammation, support a healthy metabolism, and enhance overall well-being.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Protein and Weight Management
Role of protein in weight loss
Protein is known to be the most satiating macronutrient, meaning it keeps you feeling full and satisfied for longer periods. This makes it an essential component of weight loss diets. High-protein diets can help increase metabolism, preserve muscle mass during weight loss, and promote fat loss. Including lean sources of protein, such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes, in your meals can support weight management goals.
Protein’s effect on metabolism
Proteins have a higher thermic effect compared to carbohydrates and fats, meaning they require more energy to be digested, absorbed, and transported throughout the body. This increased energy expenditure can give your metabolism a boost and contribute to weight loss. Protein also plays a role in maintaining and building muscle mass, which further supports a healthy metabolism.
Recommended protein intake
The recommended daily intake of protein varies depending on factors such as age, gender, weight, and activity level. As a general guideline, it is recommended to consume 0.8-1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, individuals engaged in regular physical activity or trying to lose weight may benefit from a slightly higher protein intake. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate protein intake for your specific needs.
Carbohydrates and Weight Management
Types of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can be classified into two main types: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods and beverages, are quickly digested and absorbed, providing a rapid energy boost. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, take longer to digest and provide sustained energy. Complex carbohydrates are generally more nutrient-dense and beneficial for weight management.
Impact of carbohydrates on weight
The impact of carbohydrates on weight depends on the type and amount consumed. Simple carbohydrates, especially those from added sugars, are often high in calories and lacking in essential nutrients. Regular consumption of these carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of chronic diseases. On the contrary, complex carbohydrates are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an ideal choice for weight management.
Choosing the right carbohydrates
When choosing carbohydrates for weight management, opt for whole grains, such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, and oats, as they provide more fiber and nutrients compared to refined grains. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, and legumes in your diet also ensures a good intake of complex carbohydrates. Be mindful of portion sizes and balance your carbohydrate intake with protein and healthy fats for optimal weight management.

This image is property of images.onlymyhealth.com.
Fats and Weight Management
Understanding different types of fats
Not all fats are created equal. There are unsaturated fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are considered healthy fats and beneficial for weight management. These fats can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. On the other hand, saturated fats and trans fats, typically found in fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty cuts of meat, should be limited as they can contribute to weight gain and health problems.
The role of fats in weight loss
Including healthy fats in your diet can actually support weight loss. Healthy fats provide a feeling of satiety, promote nutrient absorption, and help regulate blood sugar levels. By adding small amounts of healthy fats to your meals, you can increase the palatability and satiety of the foods, making it easier to stick to a balanced and calorie-controlled diet.
Optimal fat intake
The American Heart Association recommends that most of the fat in our diet should come from unsaturated fats. It is generally recommended to consume 20-35% of total daily calories from fat, with the majority being from unsaturated sources. Incorporating healthy fats into your meals, such as using olive oil for cooking or adding avocado to your salads, can help meet your fat intake needs while promoting weight management.
Fiber and Weight Management
Benefits of dietary fiber
Fiber is an indigestible carbohydrate that provides numerous benefits for weight management. It adds bulk to the diet, promoting a feeling of fullness and reducing the likelihood of overeating. Additionally, fiber aids in regular bowel movements, preventing constipation. Foods high in fiber are often low in calories, making them a great choice for weight management.
Effect of fiber on satiety
Fiber-rich foods take longer to chew and digest, prolonging the feeling of fullness. This can help control appetite and prevent excessive calorie consumption. Including fiber in each meal, such as by adding vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can enhance satiety and support weight management goals.
Recommended fiber intake
The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25-38 grams for adults. However, the average intake is often lower than recommended. To increase your fiber intake, focus on incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into your meals and snacks. Gradually increasing fiber intake and ensuring adequate fluid intake can help prevent digestive discomfort.

This image is property of www.netmeds.com.
Vitamins and Minerals in Weight Management
Importance of vitamins and minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential for overall health and well-being, including weight management. They contribute to various bodily functions, such as energy metabolism, hormone regulation, and immune system function. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods ensures an adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, supporting optimal weight management.
Their impact on weight management
Specific vitamins and minerals have been linked to weight management. For example, vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased body weight and a higher risk of obesity. Adequate intake of calcium and magnesium has also been shown to support weight loss and help maintain a healthy body weight. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products in your diet can help ensure you are meeting your vitamin and mineral needs.
Balanced Diet Tips for Weight Management
Planning meals and snacks
Planning your meals and snacks in advance can help you make healthier choices and avoid impulsive, unhealthy food decisions. Aim to include a balance of macronutrients and a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Preparing meals at home allows you to have control over the ingredients and portion sizes, making it easier to manage your weight.
Portion control
Portion control is crucial for weight management. Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if eaten in excess. Use measuring cups, kitchen scales, or simple visual cues to ensure you are consuming appropriate portion sizes. Eating slowly and paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues can also help prevent overeating.
Incorporating fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are low in calories and rich in essential nutrients and fiber. Aim to incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals and snacks. They can add volume and bulk to your diet, helping you feel satisfied while managing your weight. Experiment with different cooking methods, such as roasting or grilling, to enhance the flavors and textures of your produce.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is important for overall health and weight management. Many people often mistake thirst for hunger and end up consuming excess calories. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day and consider incorporating hydrating foods, such as watermelon and cucumbers, into your diet. Limiting sugary drinks and opting for water, herbal teas, or infused water can also help manage calorie intake.
Limiting processed foods
Processed foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them detrimental to weight management. Try to limit your consumption of processed snacks, sugary beverages, and fast food. Instead, choose whole, unprocessed foods that are nutrient-dense and provide the essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber your body needs.
Moderation and balance
One of the key principles of a balanced diet is moderation and balance. It is important to enjoy your favorite foods in moderation while still focusing on nutrient-dense options. Allowing yourself occasional treats or indulgences can help you maintain a sustainable and enjoyable eating plan. Strive for balance by incorporating a variety of food groups, colors, and flavors into your meals.
In conclusion, a balanced diet plays a critical role in weight management. By understanding caloric intake, the impact of macronutrients, and the importance of essential nutrients, one can achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Incorporating protein, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants into your diet can promote satiety, regulate appetite, and support overall well-being. Remember to plan your meals, control portions, prioritize fruits and vegetables, stay hydrated, limit processed foods, and embrace moderation and balance to achieve your weight management goals.