Are you constantly feeling tired and lacking energy throughout the day? If so, it may be time to consider boosting your energy levels with vitamins. In this article, we will explore the connection between vitamins and energy, and how incorporating certain vitamins into your diet can help combat fatigue. Discover the essential vitamins that can provide a natural energy boost and unlock a renewed sense of vitality. Say goodbye to exhaustion and hello to a more energized and productive lifestyle.

This image is property of www.ecloudbiz.com.
Understanding the Link Between Vitamins and Energy
The Role of Vitamins in Energy Production
Vitamins play a crucial role in our bodies’ energy production. They act as co-factors in various biochemical reactions that convert food into energy. These reactions occur in our cells and are essential for fueling our daily activities. Without an adequate supply of vitamins, our energy levels can be compromised, leading to fatigue and a lack of vitality.
Common Types of Vitamins for Boosting Energy Levels
Several vitamins are known for their ability to boost energy levels and combat fatigue. These include Vitamin B Complex, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, and Zinc, among others. Each of these vitamins plays a unique role in supporting our energy production pathways and promoting overall vitality. By understanding how these vitamins work, you can effectively incorporate them into your daily routine to maximize your energy levels.
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B Complex is a group of eight B vitamins that work together to support energy production. These vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin), are involved in various metabolic processes that convert carbohydrates into glucose, the primary source of energy for our bodies. They also play a crucial role in the synthesis of red blood cells, which transport oxygen to our tissues and organs, further enhancing energy levels.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is well-known for its immune-boosting properties. However, this vitamin also plays an important role in energy metabolism. It acts as a cofactor in enzymatic reactions that facilitate the breakdown of glucose, providing a steady supply of energy for our cells. Additionally, Vitamin C supports the absorption of iron, a mineral essential for energy production. By incorporating Vitamin C into your daily routine, you can enhance your energy levels and strengthen your immune system.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D, often referred to as the sunshine vitamin, is crucial for overall health and vitality. It plays a significant role in regulating calcium and phosphorus levels, which are essential for proper muscle function and energy production. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to fatigue and low energy levels. To optimize your Vitamin D levels, consider spending some time in the sun and consuming foods rich in this essential nutrient, such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects our cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Additionally, this vitamin plays a role in energy metabolism by helping to convert carbohydrates and fats into energy. By incorporating Vitamin E-rich foods, such as nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, into your diet, you can support your body’s energy production and protect your cells from damage.
Iron and Vitamin C Combination
Iron is an essential mineral for energy production as it is a key component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for transporting oxygen in our blood. Pairing it with Vitamin C enhances iron absorption, ensuring that an adequate supply reaches our cells to support energy production. Including iron-rich foods like lean meats, seafood, spinach, and beans, along with Vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits and bell peppers, can help bolster your energy levels.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral that plays a vital role in energy metabolism. It acts as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions involved in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the molecule that provides energy to our cells. Magnesium also helps alleviate muscle fatigue and cramps, making it an essential nutrient for maintaining optimal energy levels. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains into your diet can help ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements.
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10, also known as CoQ10, is a naturally occurring compound found in every cell of our bodies. It plays a crucial role in the production of ATP, the primary energy molecule in our cells. CoQ10 also acts as an antioxidant, protecting our cells from oxidative damage. While our bodies can produce CoQ10, levels tend to decline as we age. Taking CoQ10 supplements can boost energy levels and support overall vitality, especially in older individuals.

This image is property of www.netmeds.com.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are essential fats that provide numerous health benefits, including improved energy levels. These fatty acids enhance blood flow, support brain health, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to higher energy levels and reduced fatigue. Including fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, as well as chia seeds and flaxseeds, in your diet can help optimize your omega-3 intake.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that plays a vital role in energy metabolism. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including those involved in converting food into energy. Zinc deficiency has been linked to fatigue and low energy levels. Including zinc-rich foods, such as oysters, red meat, nuts, and seeds, in your diet can help ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements and supporting optimal energy production.
Adaptogenic Herbs
Adaptogenic herbs are a group of plants known for their ability to help the body adapt and respond to stress. These herbs, including ginseng, ashwagandha, and rhodiola rosea, have been traditionally used to increase energy levels, reduce fatigue, and promote overall well-being. They work by modulating the body’s stress response, balancing hormone levels, and supporting the immune system. Incorporating adaptogenic herbs into your daily routine, either in supplement form or as herbal teas, can help enhance your energy levels and improve your body’s resilience to stress.
Benefits of Vitamin B Complex for Energy
Vitamin B Complex offers several benefits when it comes to boosting energy levels. The B vitamins play a crucial role in fueling our cells by converting carbohydrates into glucose, the primary source of energy. They also support the synthesis of red blood cells, ensuring that oxygen is efficiently delivered to our tissues and organs. In addition to enhancing energy production, Vitamin B Complex can help improve mood, support brain health, and promote healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Boosting Energy Levels with Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that not only supports our immune system but also plays a role in energy metabolism. This vitamin acts as a cofactor in enzymatic reactions that break down glucose, providing a steady supply of energy to our cells. Furthermore, Vitamin C enhances iron absorption, optimizing oxygen transport and energy production. By incorporating Vitamin C-rich foods or supplements into your daily routine, you can elevate your energy levels while keeping your immune system strong.
The Role of Vitamin D in Energy Metabolism
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in energy metabolism by regulating calcium and phosphorus levels, which are essential for muscle function and energy production. Low levels of Vitamin D have been associated with fatigue and low energy levels. To ensure optimal Vitamin D levels, spend some time outdoors in the sun, especially during the summer months. Additionally, consuming Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks can help support your energy metabolism.
Enhancing Energy with Vitamin E
Vitamin E, renowned for its antioxidant properties, is also involved in energy metabolism. It helps convert carbohydrates and fats into energy, ensuring a steady supply for our cells. Additionally, Vitamin E protects our cells from oxidative damage, allowing them to function optimally. Incorporating Vitamin E-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils into your diet can help enhance your energy levels while safeguarding your cells from harm.
The Synergy of Iron and Vitamin C for Energy
Iron and Vitamin C work synergistically to support energy production. Iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in our blood. Vitamin C enhances iron absorption from food, ensuring an adequate supply reaches our cells for energy production. Combining iron-rich foods like lean meats, seafood, spinach, and beans with Vitamin C-rich foods such as citrus fruits and bell peppers can greatly enhance your energy levels.

This image is property of dta0yqvfnusiq.cloudfront.net.
Magnesium: An Essential Mineral for Energy
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in energy metabolism. It acts as a cofactor in enzymatic reactions involved in the production of ATP, the energy currency of our cells. Magnesium also helps alleviate muscle fatigue and cramps, making it crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels. Including magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains in your diet can help ensure you’re meeting your daily magnesium requirements and experiencing sustainable energy levels.
Coenzyme Q10: Energizing the Cells
Coenzyme Q10, or CoQ10, is a compound found in every cell of our bodies that plays a crucial role in energy production. It aids in the production of ATP, the molecule that provides energy to our cells. As we age, our bodies produce less CoQ10, leading to reduced energy levels. Taking CoQ10 supplements can help restore and sustain energy levels, especially in older individuals. Additionally, CoQ10 acts as an antioxidant, protecting our cells from oxidative damage.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Improved Energy
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, offer numerous health benefits, including improved energy levels. These essential fats enhance blood flow, support brain health, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to higher energy levels and reduced fatigue. Including fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, as well as chia seeds and flaxseeds, in your diet can help optimize your omega-3 intake and enhance your overall energy levels.
Increasing Zinc Intake for Energy
Zinc is a mineral that plays a vital role in energy metabolism. It is involved in various enzymatic reactions that convert food into energy. Zinc deficiency has been linked to fatigue and low energy levels. Ensuring an adequate intake of zinc through foods like oysters, red meat, nuts, and seeds can help optimize your energy production and support overall vitality.
Harnessing Energy with Adaptogenic Herbs
Adaptogenic herbs have a long history of use in traditional medicine to improve energy levels and combat fatigue. These herbs, including ginseng, ashwagandha, and rhodiola rosea, work by helping the body adapt and respond to stress. They modulate the stress response, balance hormone levels, and support the immune system. Incorporating adaptogenic herbs into your daily routine, either through supplements or as herbal teas, can help boost your energy levels and improve your body’s resilience to stress.
Sources of Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B Complex can be obtained from various food sources. Good sources of B vitamins include whole grains, beans, lentils, leafy green vegetables, meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can ensure that you’re meeting your daily requirements of Vitamin B Complex and supporting your energy production.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is abundant in various fruits and vegetables. Citrus fruits, such as oranges and grapefruits, are well-known sources of Vitamin C. Other excellent sources include strawberries, kiwis, papayas, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help ensure you’re getting an adequate intake of Vitamin C to support your energy metabolism.
Getting Enough Vitamin D
While our bodies can produce Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, it can be challenging to obtain enough through sunlight alone, especially during winter months or for those living in northern latitudes. Fortunately, Vitamin D can also be obtained through dietary sources. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of Vitamin D. Fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and mushrooms exposed to ultraviolet light are also good options for obtaining this essential vitamin.

This image is property of draxe.com.
Natural Sources of Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in various foods, with plant-based oils being the richest sources. Wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, and safflower oil are particularly high in Vitamin E. Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts, are also good sources. Including these foods in your diet can help ensure you’re consuming enough Vitamin E to support your energy levels and protect against oxidative damage.
Iron-Rich Foods and Vitamin C
Iron can be found in both plant-based and animal-based foods, with the latter being more readily absorbed by the body. Good sources of iron include lean meats, seafood, organ meats, legumes, spinach, and fortified cereals. To enhance iron absorption, it is beneficial to pair these foods with a source of Vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, bell peppers, and berries. This synergistic combination can boost your energy levels by optimizing iron uptake and utilization.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
Magnesium can be found in a variety of foods, including leafy green vegetables such as spinach and kale, nuts and seeds like almonds and pumpkin seeds, legumes, whole grains, and dark chocolate. By incorporating these magnesium-rich foods into your diet, you can help support your energy metabolism and maintain healthy energy levels.
Obtaining Coenzyme Q10 from Food
Coenzyme Q10 is naturally present in various foods, with organ meats, such as liver and heart, being the richest sources. Other good sources include fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, beef, pork, chicken, and peanuts. Consuming these foods can provide your body with CoQ10, supporting energy production and overall vitality.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Sources
Omega-3 fatty acids can be obtained from both plant-based and animal-based sources. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are rich in EPA and DHA. Plant-based sources include chia seeds, flaxseeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts, although these provide a different form of omega-3 called ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). By incorporating a combination of these foods into your diet, you can optimize your omega-3 intake and support improved energy levels.
Zinc-Rich Foods to Boost Energy
Zinc can be obtained from both animal-based and plant-based foods. Good sources of zinc include oysters, beef, pork, chicken, legumes, nuts, and seeds. By including these foods in your diet, you can support your energy metabolism and ensure you’re meeting your daily zinc requirements.
Herbal Remedies for Energy
There are several adaptogenic herbs that can be used as herbal remedies to support energy levels. Ginseng, both Asian and American varieties, is widely recognized for its energizing properties. Ashwagandha, an herb commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine, is known to reduce fatigue and improve stamina. Rhodiola rosea, another adaptogenic herb, has been shown to enhance physical and mental performance, reducing the perception of fatigue. Harnessing the power of these herbal remedies can be an effective way to naturally boost your energy levels and combat fatigue.
Recommended Daily Dosages of Vitamin B Complex
The recommended daily dosages of Vitamin B Complex can vary depending on age, sex, and individual needs. Generally, the daily recommended intakes are as follows:
- B1 (thiamine): 1-1.2 mg
- B2 (riboflavin): 1.3-1.7 mg
- B3 (niacin): 14-16 mg
- B5 (pantothenic acid): 5 mg
- B6 (pyridoxine): 1.3-1.7 mg
- B7 (biotin): 30 mcg
- B9 (folate): 400-600 mcg
- B12 (cobalamin): 2.4-2.8 mcg
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the optimal dosage for your specific needs and to ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements of these important vitamins.
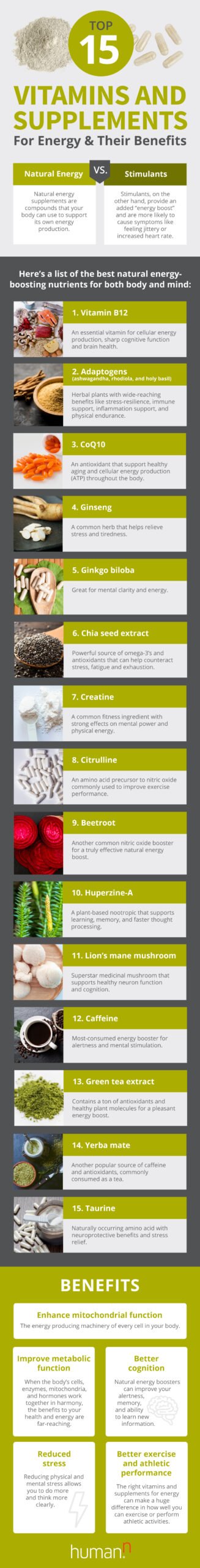
This image is property of images.humann.com.
The Recommended Intake of Vitamin C
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin C varies depending on age and sex. For most adults, the recommended daily intake is around 75-90 mg for women and 90-120 mg for men. However, during times of illness or increased stress, higher doses may be beneficial. It’s important to remember that Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, so any excess is excreted through urine. This makes it essential to consume Vitamin C-rich foods or supplements regularly to maintain optimal levels.
Vitamin D Supplements and Dosages
Vitamin D supplementation may be necessary, especially for individuals who have limited sun exposure or have higher risk factors for deficiency. The recommended daily dosage of Vitamin D varies based on age and individual needs:
- Infants (0-12 months): 400-1,000 IU (International Units)
- Children (1-18 years): 600-1,000 IU
- Adults (19-70 years): 600-800 IU
- Adults over 70 years: 800-1,000 IU
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage based on your specific circumstances and to monitor your Vitamin D levels regularly.
Recommended Vitamin E Intake
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin E for adults is around 15 mg of alpha-tocopherol equivalents (ATE). However, this can vary depending on age, sex, and individual needs. It’s important to note that Vitamin E comes in various forms, and the ATE measurement reflects the biologically available forms. To ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements of Vitamin E, incorporate Vitamin E-rich foods into your diet or consider supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Iron and Vitamin C Dosage Guidelines
The recommended daily intake of iron varies depending on age and sex. For adult males, the recommended intake is around 8 mg, while females of childbearing age (14-50 years) need 18 mg to account for menstrual blood loss. Pregnant women should aim for 27 mg, and lactating women require 9-10 mg. To enhance iron absorption, consume Vitamin C along with iron-rich foods or supplements. The recommended daily intake of Vitamin C ranges from 75-120 mg for most adults.
Recommended Daily Allowance of Magnesium
The recommended daily allowance of magnesium varies by age and sex:
- Adult males (19-30 years): 400-420 mg
- Adult females (19-30 years): 310-320 mg
- Adult males (31 years and older): 420-320 mg
- Adult females (31 years and older): 310-320 mg
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual needs may vary. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine your specific magnesium requirements and guide you in meeting them effectively.
Coenzyme Q10 Dosage Recommendations
The appropriate dosage of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) can depend on various factors, including age, health status, and specific needs. While there is no established daily recommended intake, typical dosages range from 50-400 mg per day. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the optimal dosage for your specific circumstances, especially if you have any existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Recommended Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake
The recommended intake of omega-3 fatty acids varies based on age, sex, and individual needs. The American Heart Association recommends consuming at least two servings of fatty fish per week, providing about 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day. For individuals who do not consume fish regularly, omega-3 supplements can be considered. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage based on your specific circumstances and health goals.
Zinc Supplement Recommendations
Zinc supplement recommendations can vary depending on age, sex, and individual needs. The recommended dietary allowance for adults is around 11 mg for males and 8 mg for females. However, during times of increased zinc requirements or inadequate dietary intake, supplementation may be beneficial. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs and to ensure you’re not exceeding safe levels of zinc intake.
Adaptogenic Herbs Dosage and Usage
The dosage and usage of adaptogenic herbs can vary depending on the specific herb and form (supplement or tea). It’s important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs. The dosage typically depends on factors such as age, health status, and the desired effect. Starting with the lowest effective dose and gradually increasing if needed is often recommended.
Understanding Potential Side Effects
While vitamins are generally safe when consumed in appropriate amounts, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects. Excessive intake of certain vitamins can lead to adverse effects. For example, excessive consumption of Vitamin B Complex can cause skin rashes, digestive issues, and nerve problems. Taking high doses of Vitamin C may result in stomach upset and diarrhea. Vitamin D toxicity can occur from excessive supplementation, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney problems. It’s crucial to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Interactions with Medications
Vitamins, especially when taken in supplement form, can interact with certain medications. For example, Vitamin E and Vitamin K can interfere with blood-thinning medications like warfarin. High doses of Vitamin C can interfere with certain chemotherapy drugs. Iron supplements can decrease the absorption of certain antibiotics and thyroid medications. It’s important to inform your healthcare professional about any vitamins or supplements you’re taking to ensure they don’t interfere with prescribed medications.
Precautions for Specific Health Conditions
Individuals with specific health conditions need to take precautions when supplementing with vitamins. For example, individuals with kidney problems may need to monitor their Vitamin D intake due to its potential effects on calcium levels. People with hemochromatosis, a condition characterized by excessive iron absorption, should avoid iron supplements unless explicitly recommended by a healthcare professional. Pregnant or lactating women should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosages and safe intake levels for each vitamin.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you’re unsure about which vitamins to incorporate into your routine or if you have a specific health condition, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your individual needs, review your medical history, and provide personalized recommendations based on your unique circumstances. A healthcare professional can also help determine appropriate dosages and guide you in selecting high-quality supplements if necessary.
Choosing the Right Supplements
When selecting supplements, it’s crucial to choose high-quality products from reputable manufacturers. Look for supplements that have undergone third-party testing for purity and potency to ensure you’re getting a safe and effective product. Consider factors such as the form of the supplement (pill, capsule, powder), the dosage, and any potential allergens. It’s also important to read labels carefully and follow the recommended dosages to avoid exceeding safe levels.
Combining Vitamins Strategically
Combining vitamins strategically can enhance their individual benefits and promote synergistic effects. For example, pairing iron-rich foods with Vitamin C-rich foods can optimize iron absorption and support energy production. Additionally, taking a B vitamin complex that includes all eight B vitamins can provide comprehensive support for energy metabolism. By understanding how vitamins interact with one another, you can strategically combine them to maximize their impact on your energy levels and overall well-being.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet for Optimal Energy Levels
While vitamins play a crucial role in energy production, it’s essential to remember that they are most effective when consumed as part of a balanced diet. A diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods provides the necessary vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients for optimal energy levels. By incorporating a range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet, you can ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs and supporting your body’s energy production.