Imagine if you could fight inflammation simply by choosing the right foods to include in your daily meals. Well, good news! The anti-inflammatory diet is here to do just that. By making conscious choices about what you eat, you can provide your body with the necessary nutrients to combat inflammation and promote overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of the anti-inflammatory diet and discover the delicious and nutritious foods that can help in reducing inflammation. So, get ready to discover a world of flavorful possibilities that will not only satisfy your taste buds but also leave you feeling healthier and happier.

This image is property of content.health.harvard.edu.
Understanding Inflammation
Inflammation is a normal process that occurs in the body as a response to injury or infection. It is the body’s way of protecting itself and promoting healing. When you sprain your ankle, for example, you may notice redness, swelling, and pain. These symptoms are a result of inflammation.
Inflammatory Response
The inflammatory response is a complex series of events that occur when the body detects an injury or infection. It involves the release of chemicals called cytokines, which help regulate the immune response and promote inflammation. Blood vessels in the affected area become more permeable, allowing immune cells to enter and fight off any potential threats.
Inflammation is generally a short-term process, resolving once the injury or infection has been cleared. However, in some cases, inflammation can become chronic.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a persistent state of inflammation that can last for months or even years. It is often the result of an underlying health condition, such as autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or certain types of cancer. Chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
The Role of Diet in Inflammation
While inflammation is a natural process, certain lifestyle factors, including diet, can influence its intensity and duration. Research suggests that some foods can promote inflammation, while others have anti-inflammatory properties.
Inflammatory Foods
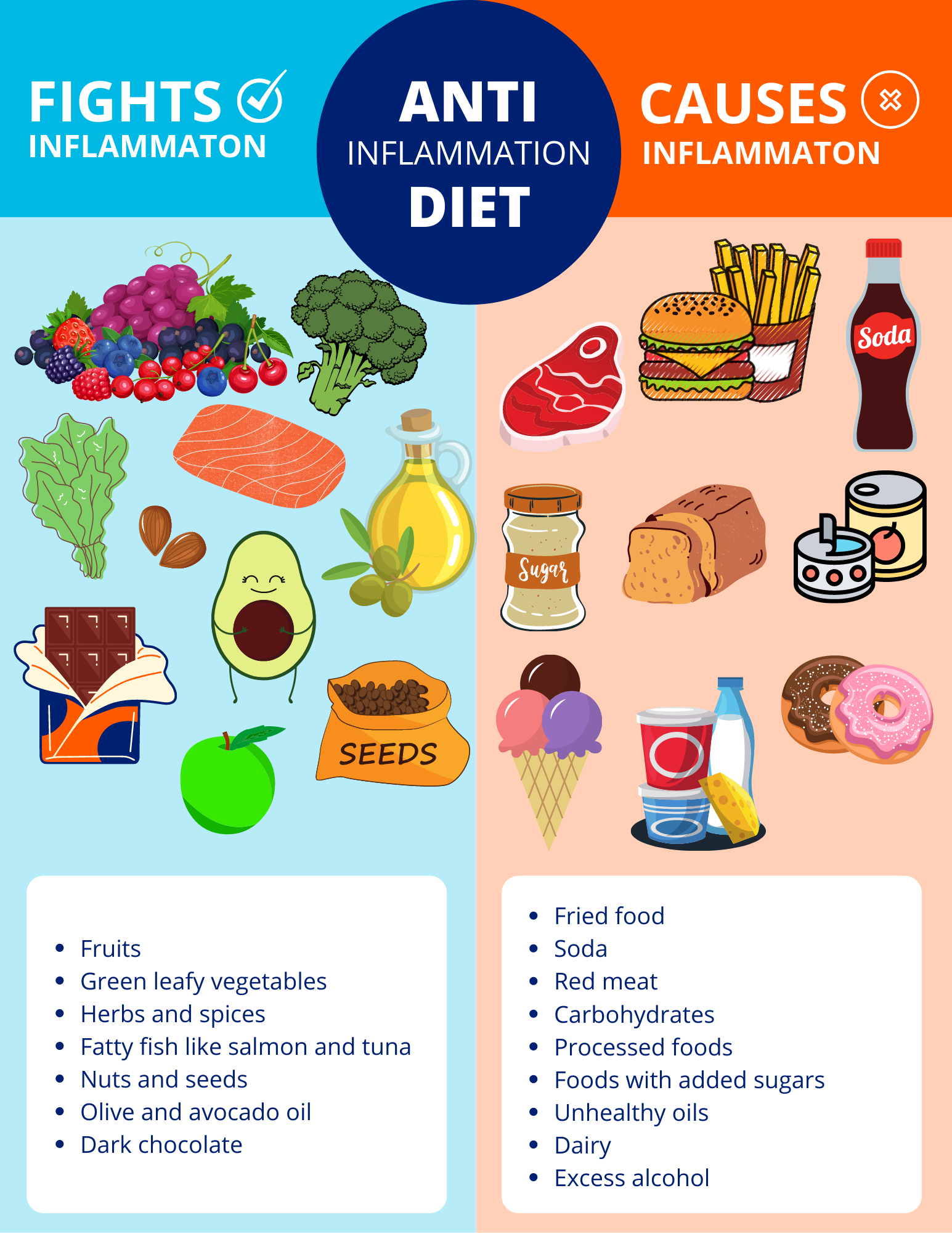
Inflammatory foods are those that can trigger or worsen inflammation in the body. These include processed foods high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars, as well as unhealthy fats like trans fats and saturated fats. Red meat, sugary beverages, and fried foods are also known to promote inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory Foods
On the other hand, anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. These foods are typically rich in antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats are all examples of foods that can help fight inflammation.

This image is property of post.healthline.com.
The Basics of an Anti-inflammatory Diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet involves making some key changes to your eating habits. Here are the basics of what you should focus on:
Balancing Macronutrients
A balanced intake of macronutrients – carbohydrates, protein, and fat – is important for overall health and can also help in reducing inflammation. Aim to include a variety of foods from each macronutrient group in your meals.
Choosing the Right Fats
Including healthy fats in your diet is essential for fighting inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, have been shown to have strong anti-inflammatory properties. Sources of omega-3s include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout, as well as chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Increasing Fiber Intake
Fiber is beneficial for overall gut health and can also help reduce inflammation. Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can promote a healthy gut microbiome and decrease levels of inflammatory markers in the body.
Components of an Anti-inflammatory Diet
To effectively reduce inflammation, it is important to focus on incorporating specific foods into your diet. Here are some key components of an anti-inflammatory eating plan:
Fruits and Vegetables
Colorful fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help combat inflammation. Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are particularly rich in antioxidants and have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects.
Whole Grains
Replacing refined grains with whole grains can provide numerous health benefits, including a reduction in inflammation. Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats are rich in fiber and other nutrients that support a healthy inflammatory response.
Healthy Fats
In addition to omega-3 fatty acids, incorporating other healthy fats into your diet can also help fight inflammation. Olive oil, avocados, and nuts, such as almonds and pistachios, are all excellent sources of healthy fats.
This image is property of www.hackensackmeridianhealth.org.
Specific Foods with Anti-inflammatory Properties
While following an overall anti-inflammatory diet is important, there are certain foods that have been specifically studied for their powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Here are a few examples:
Berries
Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are not only delicious but also loaded with antioxidants and nutrients. These fruits have been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, making them an excellent addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.
Leafy Greens
Leafy green vegetables, including spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, are nutrient powerhouses that can help fight inflammation. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a brightly colored spice commonly used in Indian cuisine. It contains a compound called curcumin, which has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory properties. Including turmeric in your diet, either through cooking or as a supplement, may help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of chronic diseases.
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is crucial for maintaining good health. They have been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory effects and can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Here are some sources of omega-3 fatty acids:
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are among the best sources of omega-3s. These fish are rich in EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), two types of omega-3 fatty acids that have been shown to have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are tiny black seeds that are packed with essential nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids. They can be easily incorporated into your diet by adding them to smoothies, cereals, or yogurt.
Walnuts
Walnuts are not only a tasty snack but also a great source of omega-3 fatty acids. They also contain other beneficial compounds like antioxidants and fiber, making them an excellent addition to an anti-inflammatory eating plan.

This image is property of d16qt3wv6xm098.cloudfront.net.
Powerful Anti-inflammatory Herbs and Spices
In addition to incorporating certain foods into your diet, herbs and spices can also play a role in reducing inflammation. Here are a few examples:
Ginger
Ginger is a pungent spice known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It contains a compound called gingerol that has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body. Adding fresh ginger to your meals or enjoying a cup of ginger tea can provide anti-inflammatory benefits.
Garlic
Garlic has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. It contains sulfur compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Including garlic in your diet, either cooked or raw, can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a warm and aromatic spice that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Sprinkling cinnamon on your morning oatmeal or adding it to baked goods can provide a delicious and healthy way to fight inflammation.
Avoiding Inflammatory Foods
In addition to incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, it is also important to limit or avoid certain foods that can promote inflammation. Here are some examples:
Processed Foods
Processed foods, such as packaged snacks, sugary cereals, and fast food, are often high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and refined grains. These ingredients can trigger inflammation and contribute to chronic diseases. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible can help reduce inflammation.
Sugar
Consuming excessive amounts of sugar has been linked to increased inflammation in the body. This includes added sugars found in processed foods, sugary beverages, and desserts. Choosing natural sweeteners like honey or opting for fruit as a sweet treat can help satisfy your cravings while reducing inflammation.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are a type of unhealthy fat that is found in many processed and fried foods. They have been shown to promote inflammation and increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. Reading food labels and avoiding products that contain partially hydrogenated oils can help reduce your consumption of trans fats.

This image is property of health.clevelandclinic.org.
The Impact of Gut Health on Inflammation
The health of your gut plays a crucial role in inflammation and overall well-being. A healthy gut microbiome has been associated with a reduced risk of inflammatory diseases. Here are some factors to consider:
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help promote a healthy gut microbiome. Consuming foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can help support a balanced gut and reduce inflammation.
Prebiotic Foods
Prebiotics are types of fiber that act as fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. They can be found in foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus. Including prebiotic-rich foods in your diet can help nourish the good bacteria in your gut and improve overall gut health.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods, such as sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha, contain beneficial bacteria that can help promote gut health. Including these foods in your diet can provide additional support for reducing inflammation and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
Incorporating an Anti-inflammatory Diet into Your Lifestyle
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet doesn’t have to be complicated or restrictive. Here are some tips for incorporating this eating plan into your lifestyle:
Meal Planning
Plan your meals ahead of time to ensure you have a variety of anti-inflammatory foods on hand. This can help you make healthier choices and prevent relying on unhealthy convenience foods when hunger strikes.
Cooking Techniques
Opt for cooking methods that preserve the nutritional value of your food. Steaming, sautéing, and baking are all healthy cooking techniques that can help retain the beneficial compounds in your ingredients.
Mindful Eating
Practicing mindful eating can help you tune in to your body’s hunger and fullness cues and make more conscious choices about the foods you eat. Slow down, savor your meals, and pay attention to how different foods make you feel.
By incorporating these strategies and making small, sustainable changes to your eating habits, you can support your body’s natural inflammatory response and promote overall health and well-being. Remember, an anti-inflammatory diet is just one piece of the puzzle for reducing inflammation, so be sure to consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized approach that suits your specific needs and health conditions.
